Although it is essential to have SEO optimized pages on Google, this is almost never enough to get the results you want. Off-page optimization (outside our pages), essentially concerns the management of links on other websites that link to ours (backlinks).
In the 90s, the two Google founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, based their success on the belief that the pages with a greater number of backlinks were the most important and worthy. This was really the great Google innovation, which changed the internet search market forever. In Google’s eyes, a link to a page is essentially a “vote” for its content. In other words, it expresses the willingness, by the webmaster or site owner, to link back to an important resource worthy of being visited by users .
The logical consequence is that one of the main factors affecting Google’s ranking is the number of links pointing to a website. However, the importance of a website is not entirely calculated on the amount of backlinks. Google also considers the importance of the link source. A link from an influential page is worth more than one from a low quality website. It is therefore theoretically possible to be positioned better than a competitor with fewer links, if these are of sufficiently high quality.
To calculate the importance of a page, and consequently the quality of a link, Google came up with a formula called PageRank: each webpage gets a “vote” from 0 to 10 to according to the number of links. The PageRank formula for years remained secret and was then disclosed by Google. Below is a simplified version of the formula:
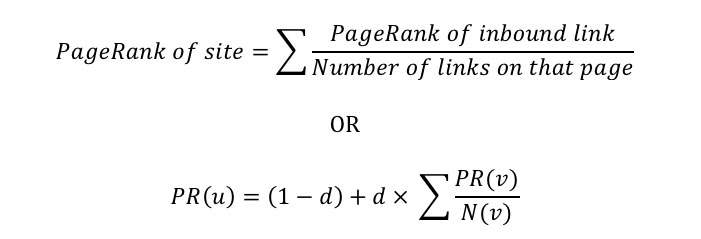
Simplified version of the PageRank formula
Where:
- PR (u) is the value of the PageRank of the page u that we want to estimate.
- PR (v) is the value of the PageRank of each pages that connects the page u.
- N (v) is the total amount of outbound links within the page where our link is.
- d (damping factor) is a factor established by Google and represents the possibility for users to not follow any link. It normally takes the value of 0.85, but it can be modified by Google for any specific case.
From the formula we can see that as the number of total backlinks pointing to u increases, the PageRank increases. But it also depends on the PageRank of the individual pages that link to u and on the number of outbound links from those pages.
For a further simplification, we can say that the higher the PageRank of the pages that link to us is (and the number of pages that link to us), the higher our PageRank will be. A high PageRank, although less important than in the past, is still a factor that Google takes into consideration to position the pages in its ranking.
In addition to the quantity and the quality of the links received, there are other factors related to links that affect the organic positioning. In addition to being a “vote” of quality, the link is in fact – for search engines – also a thematic information.
Google SEO
With this in mind, there are two more factors that determining the value of each link pointing to our site: the topic of the referring page and the anchor text of the link. An inbound link (to our site), in order to have an effective value for us, will have to come from a page that deals with the same topic (or as closely as possible) as ours.
For the same reason the anchor text, which is the word/words that form the link (and therefore the clickable ones), must be relevant to the topic we are dealing with. For example, if our goal is to position ourselves with the keyword “positioning on Google”, the maximum value for us is to receive links with the anchor text containing the words “positioning on Google”, that is also our reference keyword. In this way, the search engine will consider our relevant page with that query.
The “off-page” activity therefore consists mostly of managing the link pupularity, a very important part of the process. This part is often longer and more difficult than the “on-page” part, since we do not have direct control over other webistes. To manage link popularity, as we have said, it is necessary to obtain links to your website from other websites that are relevant and relevant to the topic covered by the site. But how do we do it?
Link popularity management is built up through actions more or less compliant with Google guidelines and this is the subject of numerous debates.
Link earning vs link building
As links are signs of interest, it is clear that getting links is a natural consequence of having quality content on your site. But on the other hand, the acquisition of spontaneously inserted links could be a slow process.
For this reason, many SEOs have over the years devised different tactics to get links from other sites in a non-spontaneous way. The combination of these tactics is called link building.
These techniques, especially in some very competitive sectors, have been used excessively, becoming a spam phenomena. There was a time when practices such as link exchange, spam links on blogs and forums, compulsory lists of links of dubious quality were common and worked very well for SEO.
To stem these manipulative phenomena, Google is constantly updating its ranking algorithms, introducing new and increasingly sophisticated systems for detecting unnatural links and other spam techniques – the most famous of which is the algorithm called Penguin. The consequent “punishment” for these unfair behaviors is to penalize websites by lowering their ranking position.





